The environmental impact of power plants and how to reduce it

Concerns regarding the environmental impact of power plants are at an all-time high. Power plants are huge industrial facilities where electrical power is generated for distribution purposes. The source of energy used to produce electricity can be different, but most of the power plants in the world burn fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas. Other facilities use nuclear, solar, wind, wave or hydroelectric power with each of them bringing different options and different risks for human well-being and the environment too.
By far, the most used energy source to generate electricity in the US power plants is coal. At present, there are approximately 1200 coal-fired generators at 450 facilities in the country. These coal-using power plants generate nearly 45% of the country’s electricity. The worrying fact is that coal-fired power plants emit 84 of the 187 hazardous air pollutants identified by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). According to the National Toxicology Program, these pollutants may cause cancer and hazardous air pollution released by coal-fired power plants can cause a wide range of health risks, including heart and lung diseases as well.

Affecting the environment
Besides affecting human health, power plants can also affect the environment by its construction and by its operation. Together with its auxiliary components, it takes up space on the ground and in the air, using up water resources and in many cases, emitting pollutants. These effects can be either temporary or permanent. Both fossil fuel-fired and biomass-fired electricity plants burn fuels to make either hot air or steam needed to spin power turbines to generate electric power. The burning creates exhaust gases and other by-products, including air pollutants. In order to make steam, the plants need to use a large amount of water from nearby rivers, lakes or from local underground water aquifers. Because the used water must be discharged from the plant after its use, it’s very important that the power plants discharge the water in the right manner while respecting the rules and standards.
During the electrical power generation process, a variety of solid wastes can be produced and these must be handled carefully. The very combustion of coal creates ash as solid waste. On the other hand, nuclear power plants create spent nuclear fuel rods and low-level radioactive waste that needs to be discharged with proper care. Plants that use water to create steam or cooling must often filter and purify the water before discharging it. Such filtered solids are also a by-product that must be disposed of appropriately.
The planet’s ability to retain solar heat is highly dependent on concentrations of greenhouse gases (GHGs) that are found in the atmosphere. These gases in the atmosphere trap heat and help keep the planet warm enough for life to survive. The main problem is that power plants fueled by fossil fuels produce large amounts of CO2. Relevant scientists believe that increases in GHG concentrations have contributed to an additional warming of the planet and continued increases in concentrations are expected to cause further warming and a variety of global climate changes in the future.
Wetland vegetation can be greatly affected by heavy machinery. Wetland soils can easily be affected, increasing runoff and reducing the wetland’s water holding capacity. The construction of power plant access roads through wetlands can change the quantity of direction of water flow, causing permanent damage to wetland soils and vegetation. It’s pretty safe to say that sites with no wetlands or no potential for adverse wetland effects are preferred for such plants.
How to reduce environmental impact?
Power plant operators and owners have a range of systems available to reduce pollutants at their facilities. As environmental regulations designed to control emissions from power plants led to the development of a range of technologies to control pollutants, these technologies have evolved as regulations have changed during the years.
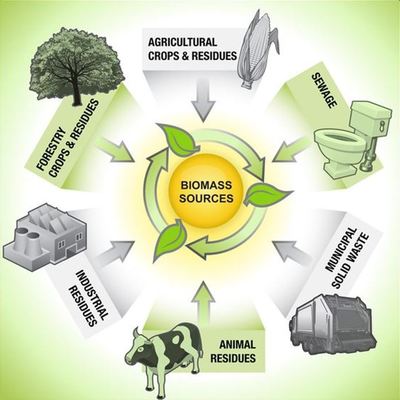
Different states have considerable flexibility in how they comply with the EPA’s power plant emission standards. The main field of these standards is lowering the emissions of CO2 - including greater use of existing lower-carbon power plants, increased use of renewable sources, energy efficiency and other strategies. Being very successful in converting energy plants from coal, natural gas, and other energy sources into alternative green energy sources known as biomass, Industrial Boilers America is one of the key players on the market when it comes to using industrial biomass boilers. The use of biomass boilers in heating systems is super beneficial as it uses solely forest, agricultural, industrial and urban residues and waste to produce heat and electricity with less effect on the environment than fossil fuels.
This new generation of energy processes, called ‘clean coal technology’ has the ability to reduce air emissions and other pollutants. These technological breakthroughs make it possible for older coal-burning power plants to produce electricity in an environmentally responsible and economical manner. There are few options available for use alone or in combination such as: optimizing existing plants so they reduce emissions and increase the amount of electricity produced with the same amount of coal; gasification - turning coal into a gas and removing impurities from the coal gas before it’s combusted; development of the best-available combustion technology including circulating fluidized-bed technology; carbon capture and storage (CCS).
Utilities can implement programs that help customers save energy at their homes and businesses. Meeting such standards can reduce CO2 emissions by 11% in ten years’ time. Industrial manufacturers, hospitals, universities, and similar businesses can save energy by installing combined heat and power systems which generate electricity more efficiently than the average power plants.
With the increase of optimization, analytics, and digital twin monitoring technology, the right software technologies can complement and replace the costly capital investments in achieving compliance and sustainability goals. Technologies such as the advanced process control can improve combustion efficiency and a power plant’s generation capacity while also cutting emissions. Advanced process control can take care of combustion, cooling, and every other process much closely than conventional control systems, enabling the operator to run the units, turbines, and related systems with much lower variability and much closer to design specifications.



